Synopsis: The Black-Scholes model helps investors make sense of option pricing, showing how factors like stock price, volatility, time, and interest rates determine value today. It doesn’t predict market moves but gives a clear framework to manage risk and make smarter trading decisions, even in a market that rarely follows the rules.
Money on Dalal Street often appears to move without rhyme or reason. Sudden spikes, sharp drops, and rapid swings create the impression of chaos, yet beneath this volatility lies a framework that quietly governs pricing, risk, and market behaviour. The true edge in investing rarely comes from predicting price movements; it comes from understanding how prices are determined and the forces that shape them.
For retail investors, the challenge is not always selecting the right stock, but navigating the hidden mechanics of risk and timing. A stock can climb, yet gains may evaporate due to factors such as market volatility and the passage of time. There exists a mathematical principle that explains the current value of assets based on these forces. It does not forecast direction, but it decodes the logic behind pricing, knowledge that can fundamentally change how an investor approaches the market.
What Is Black Scholes Model
Every financial market is built around one basic challenge: how do you price something today when its value depends on what might happen tomorrow? That is the problem this equation was designed to solve.
Think of it like a concert ticket that gives you the right to attend a show next month at today’s price. You don’t know whether the artist will become wildly popular or fade from attention. Yet that right has a value today, shaped by time, uncertainty, and current prices. The model applies the same logic to financial markets.
Rather than trying to predict where a stock will go, the equation focuses on what a future right linked to that stock should be worth right now. It uses a small set of observable inputs: the current stock price, the price at which it can be bought or sold later, the time remaining, how much the stock typically fluctuates, and a risk-free benchmark return. Together, these variables help estimate a fair price.
The key idea is risk, not forecasting. The model assumes that stock prices move continuously and that their ups and downs follow a measurable pattern over time. Based on this, it allows market participants to set prices that reflect uncertainty instead of emotion. This is why the equation became so widely used. It didn’t claim to know the future. It provided a disciplined way to price it. It explains value, not direction.
What Is The Formula Behind It
The Black-Scholes model is a mathematical formula used to calculate what an option should be worth. While the math behind it can look complicated, you don’t need to understand all the equations to use it. The model helps traders estimate the fair price of an option based on a few key factors: the current stock price, the option’s strike price, the time left until expiry, how much the stock typically fluctuates, and the risk-free interest rate. It focuses on valuing the option today rather than trying to predict where the stock will go.
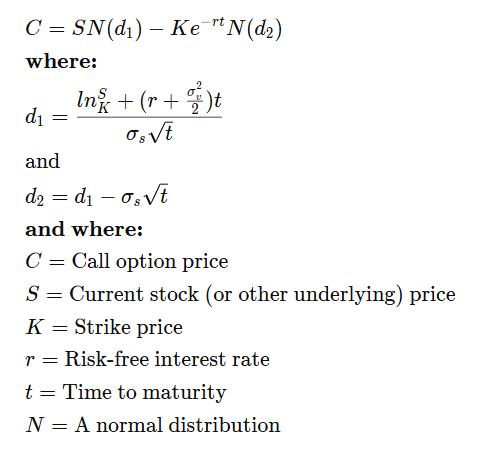
SOURCE: INVESTOPEDIA
Online Calculators
Most traders don’t calculate the formula by hand. Instead, they rely on online calculators or trading platforms that automatically do all the math. One popular tool for Indian investors is the Zerodha Black-Scholes calculator, which allows you to input the spot price, strike price, time to expiry, volatility, dividend, and risk-free rate. The calculator then instantly gives the theoretical price of the option.
The calculation works by first adjusting the stock price for the probability that the option will end up in the money and then subtracting the strike price, discounted to its present value and adjusted for probability. This gives the option’s fair value under current market conditions.
In essence, the Black-Scholes model is a structured way to put a price on uncertainty. It doesn’t guess the stock’s direction but provides a disciplined method to determine how much a future right, like a call or put option, is worth today. With the Zerodha calculator, traders and retail investors can easily use this model without worrying about the complex mathematics
Assumptions of The Model
The model is built on a few key assumptions to make option pricing possible. It assumes that stock prices follow a lognormal distribution, meaning they can never go below zero. The model also assumes that stocks do not pay any dividends and that options are exercised only at expiry, which makes it suitable for European-style options.
In India, index options like NIFTY and BANKNIFTY follow this European exercise style, so the model works well for them. Stock options, on the other hand, are American-style and allow early exercise, so the model isn’t perfect for them, but it still gives a useful approximation since early exercise is not very common.
The model also assumes that the stock market behaves like a random walk, meaning its direction cannot be predicted. It ignores transaction costs such as brokerage and commissions, and it assumes that interest rates are constant, treating the underlying asset as risk-free. Additionally, the model expects stock returns to be normally distributed, which implies that market volatility remains constant over time.
Another important assumption is that there is no arbitrage, meaning there is no way to make a risk-free profit from price differences in the market. These assumptions simplify reality, allowing traders to use the Black-Scholes model as a practical tool to estimate fair option prices, even though real markets may not perfectly follow all these rules.
How You Can Up Your Option Game
The Black-Scholes model offers several advantages that make it widely used by financial professionals. It provides a clear and structured framework for pricing options, allowing investors and traders to determine a fair value using a method that has been tried and tested over time.
By knowing the theoretical value of an option, investors can better manage their risk exposure, evaluate potential returns, and identify weak areas in their portfolio. This helps in making more informed decisions and understanding where their investments may be vulnerable.
The model also supports portfolio optimization by giving a measure of the expected returns and risks associated with different options, enabling smarter investment choices that align with risk tolerance and profit goals.
Additionally, it enhances market efficiency and transparency by providing a consistent and widely accepted method for pricing options. This streamlines the trading process, ensures comparability across different markets, and helps traders and investors operate with a clearer understanding of how option prices are derived.
Limitations You Should Watch For
The Black-Scholes model has some important limitations that can affect its accuracy. It is primarily designed for European options and does not account for the possibility of early exercise, which is allowed in American-style options. The model also assumes that dividends and risk-free interest rates remain constant, but in reality, these can change over time, making it less able to reflect the true future cash flows of an investment.
Additionally, the model assumes that volatility stays constant throughout the option’s life, even though market volatility often changes with supply and demand. It also relies on other simplifying assumptions, such as no transaction costs or taxes, constant interest rates for all maturities, permission for short selling with proceeds, and no risk-free arbitrage opportunities. Because real markets rarely follow all these rules, the Black-Scholes price can sometimes deviate from actual market prices.
Conclusion
In the fast-moving world of options trading, the Black-Scholes model acts like a compass amid the chaos. It doesn’t claim to predict where the market will go, but it helps investors put a fair price on uncertainty, turning guesswork into informed decision-making.
By factoring in elements like stock price, volatility, time, and interest rates, it gives traders a framework to manage risk and spot opportunities with clarity. That said, it’s not perfect, real markets rarely follow all its assumptions. Think of it as a guide, helping you navigate the twists and turns of trading with logic, not luck.
Disclaimer: The views and investment tips expressed by investment experts/broking houses/rating agencies on tradebrains.in are their own, and not that of the website or its management. Investing in equities poses a risk of financial losses. Investors must therefore exercise due caution while investing or trading in stocks. Trade Brains Technologies Private Limited or the author are not liable for any losses caused as a result of the decision based on this article. Please consult your investment advisor before investing.
tradebrains.in (Article Sourced Website)
#BlackScholes #Model #Traders #Level #Options #Trading

