Purpose and profit increasingly intersect, and the numbers tell a compelling story. According to the CleanHub ESG Statistics Report, 85% of investors believe ESG investments improve financial returns. This isn’t merely an ethical imperative—it’s a financial one. This presents both an opportunity and a challenge for marketing professionals: communicating sustainability initiatives while authentically driving measurable business growth.
Enter ESG marketing frameworks—environmental, social, and governance messaging. These frameworks transcend surface-level storytelling to create authentic connections with increasingly conscious consumers.
Key Takeaways
- ESG marketing has evolved from basic CSR to strategic frameworks that align sustainability with core business objectives, with research showing a 92% correlation between high ESG ratings and profitability among top-performing companies.
- Effective ESG marketing frameworks balance three critical pillars – Environmental (planet-focused messaging with specific metrics), Social (people-centered narratives with employee advocacy), and Governance (trust-building transparency through clear ethical standards).
- Four proven ESG marketing framework models include Multi-Channel Storytelling (exemplified by Patagonia), Digital Integration (used by Unilever), Employee Advocacy (leveraging internal voices), and Technology-Driven Verification (implemented by Citi using blockchain and AI).
- Implementing ESG marketing frameworks requires a 5-step approach beginning with assessment, followed by strategic goal setting, framework selection, content strategy development, and continuous measurement and refinement.
- Avoiding greenwashing is crucial for ESG marketing credibility. It can be achieved by anchoring all marketing claims in verifiable data, being transparent about progress and challenges, and obtaining third-party certifications.
The Evolution of ESG Marketing
ESG marketing has evolved significantly over the past decade. What began as disconnected corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives has transformed into comprehensive frameworks that align sustainability with core business objectives.
“The transition from traditional CSR to modern ESG frameworks represents a fundamental shift in how businesses approach sustainability communication. Today’s frameworks demand measurable outcomes, authentic storytelling, and strategic integration with business goals.”
This evolution has been driven by increasing stakeholder pressure, regulatory changes, and the growing recognition that sustainability creates business value. Research from the Center for Sustainability and Excellence (CSE) reveals a 92% correlation between medium-to-high ESG ratings and profitable companies among top-performing firms. This striking correlation demonstrates that effective ESG marketing isn’t just about projecting a positive image and fundamental business performance.
Core Components of Effective ESG Marketing Frameworks
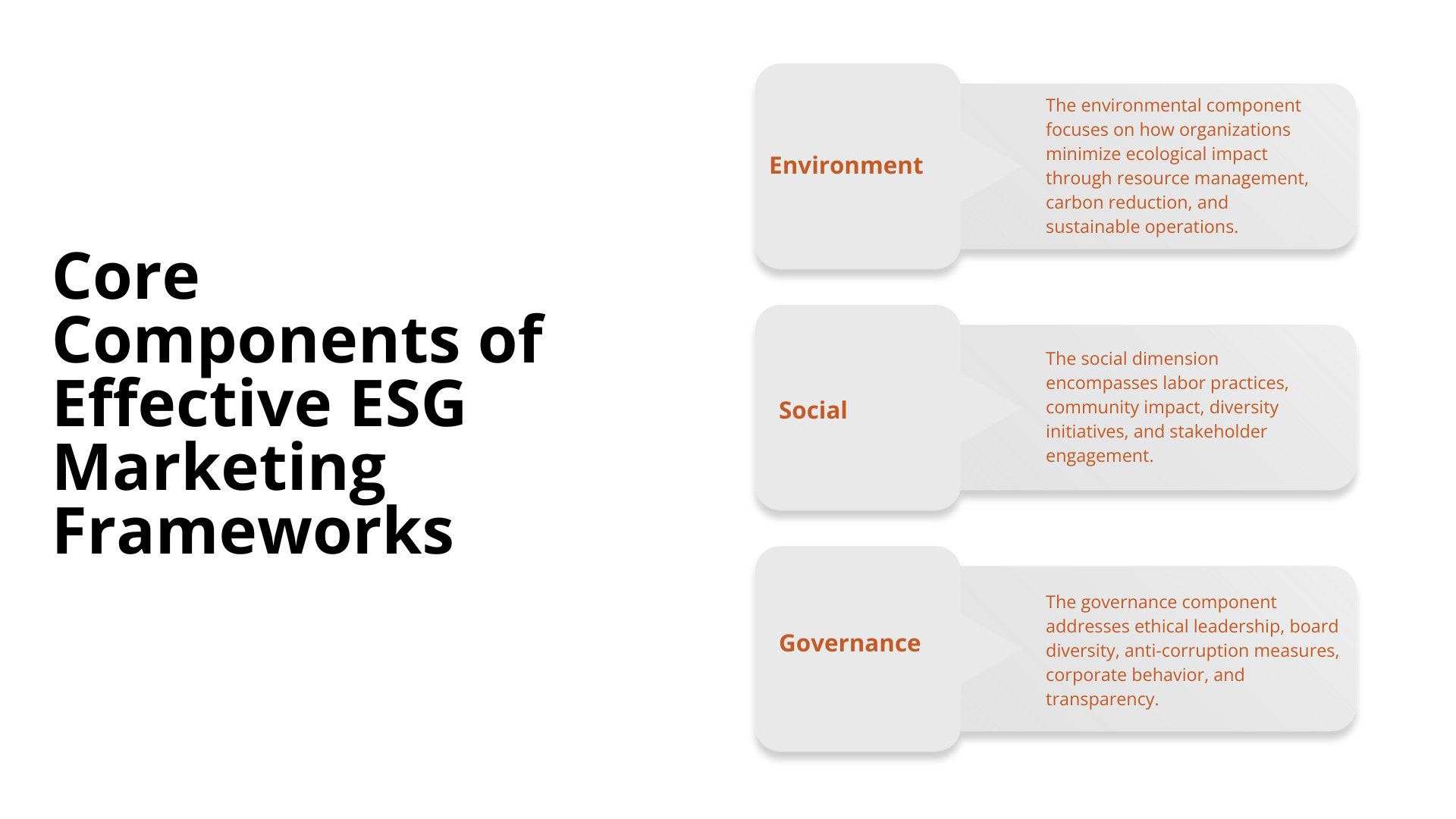
Successful ESG marketing frameworks balance three critical pillars while maintaining authentic communication throughout all of them.
Environmental Pillar: Planet-Focused Messaging
The environmental component focuses on how organizations minimize ecological impact through resource management, carbon reduction, and sustainable operations. Effective environmental marketing:
- Quantifies environmental impacts with specific metrics
- Communicates transparent goals and timelines
- Demonstrates continuous improvement rather than perfection
- Connects environmental initiatives to product or service benefits
Unilever exemplifies this approach through its Climate Transition Action Plan, which has achieved a 72% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions since 2015. Its marketing strategy embeds sustainability metrics directly into product storytelling for brands like Hellmann’s and Persil, creating authentic connections between environmental goals and consumer benefits.
Social Pillar: People-Centered Narratives
The social dimension encompasses labor practices, community impact, diversity initiatives, and stakeholder engagement. Effective social-pillar marketing:
- Amplifies internal voices through employee advocacy programs
- Demonstrates measurable community impact
- Showcases diversity across marketing channels
- Creates two-way dialogues with stakeholders
Governance Pillar: Trust-Building Transparency
The governance component addresses ethical leadership, board diversity, anti-corruption measures, corporate behavior, and transparency. Effective governance messaging:
- Communicates clear ethical standards and policies
- Publishes transparent ESG reports and metrics
- Showcases diverse leadership perspectives
- Demonstrates accountability through third-party verification
4 Proven ESG Marketing Framework Models
Several distinct ESG marketing frameworks have emerged as particularly effective. Each offers unique advantages depending on organizational goals, industry context, and target audience:
| Framework Model | Key Components | Best For | Example Brand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Channel Storytelling Framework | Authentic narrative development, channel-specific content adaptation, stakeholder journey mapping | Consumer-facing brands with strong brand identity | Patagonia |
| Digital Integration Framework | Real-time ESG metrics tracking, data visualization, integrated digital touchpoints | Tech-forward companies with robust digital ecosystems | Unilever |
| Employee Advocacy Framework | Internal engagement programs, employee content creation, authentic testimonials | Service-oriented businesses with strong internal cultures | Salesforce |
| Technology-Driven Verification Framework | AI/blockchain for data verification, real-time analytics, transparent reporting | Financial services and companies with complex supply chains | Citi |
- Multi-channel storytelling: This framework focuses on creating authentic narratives around ESG initiatives and adapting them across multiple channels. The key to this framework is aligning authentic messaging with brand values and ensuring consistency across all channels.
- Digital integration: This framework embeds ESG metrics and messaging directly into digital marketing initiatives.
- Employee advocacy: 79% of companies say employee advocacy increased online visibility. Consumers want to see companies promote sex, gender, and racial equality; the best way to do that is within. Effective implementation includes creating clear ESG communication guidelines for employees and highlighting employee involvement in sustainability initiatives.
- Technology-driven verification: As ESG claims face increasing scrutiny, technology-driven verification frameworks provide crucial transparency
ESG Marketing Frameworks: A 5-Step Guide
To implement an ESG framework, all marketers must follow these five steps to assess their current ethical stance and set goals to convey their values.
Step 1: Assessment
Begin by auditing current ESG performance across environmental, social, and governance dimensions. Assess your current practices and find areas for improvement. This is the foundation for authentic marketing claims and can identify strengths to highlight and areas for improvement.
Key actions:
- Conduct a comprehensive ESG audit using established standards
- Benchmark performance against industry peers
- Identify existing data collection mechanisms and gaps
- Assess current ESG messaging and perception
Step 2: Goal Setting
Establish clear, measurable ESG goals that align with marketing objectives and broader business strategy. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
For example, in the Unilever case study, we will mention later that the company set a goal to halve its environmental footprint while doubling its business. This provides marketing teams with clarity and measurability.
Step 3: Selection and Adaptation
Choose the ESG marketing framework that best aligns with your organization’s strengths, industry, and audience. Most successful implementations combine elements from multiple frameworks to create a custom approach.
Consider factors like:
- Existing marketing infrastructure and capabilities
- Target audience
- ESG priorities and concerns
- Industry-specific sustainability challenges
- Available resources and technology
Step 4: Content Strategy Development
Develop a comprehensive content strategy that translates ESG initiatives into compelling narratives across appropriate channels. This should include:
- Core messaging architecture for each ESG pillar
- Channel-specific content adaptations
- Visual guidelines for ESG communication
- Content calendar aligned with business initiatives
For organizations working with marketing agencies, this step often involves close collaboration to ensure ESG messaging integrates seamlessly with broader marketing efforts.
Step 5: Measuring and Refining
Launch your ESG marketing framework with clear KPIs tracking marketing performance and sustainability impact. Regular assessment allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to changing stakeholder expectations.
Brands should track KPIs that fit the environmental, social, and governance pillars. Here are some example KPIs:
Enviornmental
- Fuel consumption
- Energy use
- Greenhouse emissions
- Water consumption
- Resource efficiency
Social
- Diversity and inclusion
- Worker health and safety
- Human rights
- Compensation equality
- Labor policies
Governance
- Board and management diversity
- Disclosure and reporting programs
- Transparency of policies
Case Studies: ESG Marketing Frameworks in Action
Unilever: Digital Integration Framework
Challenge: Unilever needed to transition from broad sustainability ambitions to a precise, measurable ESG strategy integrated into digital marketing initiatives.
Solution: They refined ESG priorities under their Growth Action Plan 2030, embedding tangible sustainability metrics in digital storytelling across product lines and enhancing data reporting systems for real-time tracking.
Results: Unilever achieved a 72% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions since 2015, set ambitious Scope 3 reduction targets, and boosted consumer trust through transparent digital engagement.
Citi: Technology-Driven Verification Framework
Challenge: Citi faced increasing demands for transparency and accuracy in tracking sustainability metrics for investment products.
Solution: After partnering with ESG Book, Citi implemented AI for data analysis and blockchain for immutable, real-time tracking of ESG performance, creating a robust equity benchmark index family.
Results: Enhanced data verification, improved investor trust through real-time analytics, and attracted significant institutional interest in ESG-index products.
Patagonia: Authentic ESG Narrative Framework
Challenge: Patagonia needed to align its brand identity with environmental sustainability while effectively communicating ESG commitments in an industry where authenticity is critical.
Solution: They launched the iconic “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign that encouraged responsible consumption through repair and reuse messaging while reinforcing the brand’s commitment to sustainability.
Results: The campaign reinforced customer loyalty, significantly boosted brand awareness as an environmental leader, and set a benchmark for effective ESG-driven marketing.
Common Challenges and Solutions in ESG Marketing
Implementing ESG marketing frameworks comes with several challenges that marketing teams must navigate.
Challenge: Avoiding Greenwashing
With increasing scrutiny of ESG claims, avoiding accusations of greenwashing is crucial for maintaining credibility.
Solution: Anchor all marketing claims in verifiable data, be transparent about progress and challenges, and obtain third-party certifications where possible. Technology-driven verification frameworks can provide crucial transparency through blockchain and AI verification.
Challenge: Difficulties Measuring KPIs
ESG initiatives often involve complex, long-term impacts that can be difficult to quantify for marketing purposes.
Solution: Develop a balanced scorecard of marketing metrics (engagement, sentiment, conversion) and ESG impact metrics. Work with sustainability teams to identify meaningful proxy measurements that can be communicated effectively.
Challenge: Internal Alignment
Successful ESG marketing requires alignment between marketing, sustainability, operations, and leadership teams.
Solution: Create cross-functional working groups, develop shared ESG communication guidelines, and establish regular touchpoints between marketing and sustainability teams. The employee advocacy framework can be particularly valuable here.
Future Trends in ESG Marketing
ESG marketing continues to evolve rapidly. Forward-thinking marketers should watch for these emerging trends.
- AI-driven ESG personalization: Artificial intelligence enables increasingly sophisticated ESG messaging personalization based on individual stakeholder values and priorities. Tools like ChatGPT for marketing are helping brands create more targeted, relevant ESG content for different audience segments.
- Blockchain for credibility: Citi’s case study demonstrated that blockchain technology increasingly verifies and communicates ESG claims with unprecedented transparency. This trend will likely accelerate as consumers demand more verification of sustainability claims.
- Collaborative frameworks: Industry-wide collaborative frameworks are emerging to address systemic sustainability challenges that no organization can solve alone. These collaborative approaches often create powerful storytelling opportunities around collective impact.
Building Authentic ESG Marketing Frameworks
Companies can no longer focus solely on profits. Instead, brands must consider purpose and driving a positive impact. Implement ESG marketing frameworks that balance authenticity with marketing objectives to transform sustainability initiatives into business growth.
Looking to develop a successful ESG marketing campaign that drives real results for your organization? Work with the leading digital marketing agency specializing in data-driven, authentic marketing strategies that balance purpose with performance.
www.singlegrain.com (Article Sourced Website)
#Building #Authentic #ESG #Marketing #Frameworks #Drive #Results
