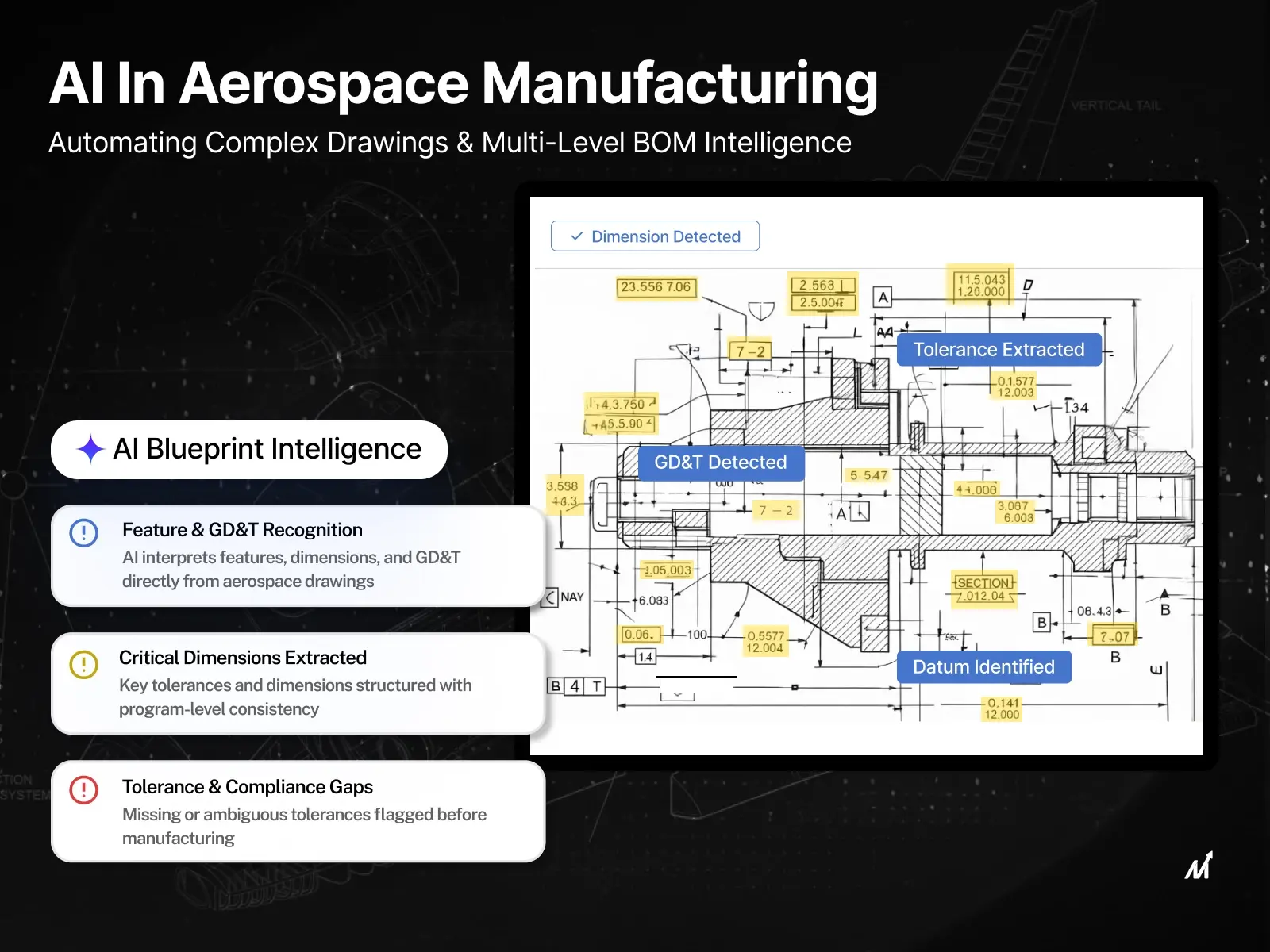
In aerospace manufacturing, complex engineering drawings form the backbone of production, compliance, and program cost control. Dense GD&T callouts, multi-level assemblies, and strict tolerance requirements make manual interpretation time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale across teams. AI in aerospace manufacturing is transforming this workflow by automatically interpreting blueprints, extracting tolerances and features, and generating structured, multi-level BOMs that align with engineering intent.
By converting raw drawing data into actionable insights, AI helps manufacturers reduce errors, accelerate RFQs, and improve coordination between engineering, quality, and supply chain teams. In this blog, we explore how enterprise-grade AI streamlines aerospace blueprint workflows, enabling organizations to achieve consistent, auditable, and scalable manufacturing operations.
Table of Contents
- Why Aerospace Manufacturing Drawings Are Uniquely Complex
- Where Manual Interpretation Breaks Down
- AI as a Blueprint Intelligence Layer
- Automating GD&T Extraction and Feature Recognition
- From Drawings to Multi-Level BOMs, Costing, and RFQs
- Rule-Driven Intelligence for Aerospace Control
- AI Blueprint Intelligence in the PLM Workflow
- Markovate’s Role in Aerospace Blueprint Intelligence
- Conclusion: AI in Aerospace Manufacturing
Why Aerospace Manufacturing Drawings Are Uniquely Complex
Aerospace drawings are not just instructions; they are system-level design intelligence. They combine structural, mechanical, electrical, and systems information across multiple views, with dense annotations that must be interpreted together.
Tight tolerances and extensive GD&T, often program-specific, directly affect compliance and airworthiness. Parts are highly interdependent, requiring consistent interpretation across assemblies and aircraft systems.
Programs span years, with continuous revisions, overlays, and legacy notation styles, making traceability critical. Even minor misreads can impact machining, inspection, and supplier execution. These factors make aerospace drawings a high-stakes challenge, demanding precision, consistency, and repeatable interpretation across teams and suppliers.
Where Manual Interpretation Breaks Down in Aerospace Programs

Aerospace manufacturing requires a consistent, system-level understanding of complex drawings. Traditional manual methods struggle to scale across multi-disciplinary programs, high-density GD&T, and tightly interdependent assemblies, thus making it challenging to maintain accuracy, compliance, and alignment across engineering, procurement, and suppliers. Let’s read the reasons in detail:
1. Interpretation varies across roles and organizations
Engineers, estimators, quality teams, and external suppliers often interpret the same drawing differently. These variations introduce misalignment early, long before parts reach the shop floor or inspection.
2. Manual BOM creation introduces structural risk
Extracting multi-level BOMs from drawings is time-intensive and error-prone. Missing components, duplicated entries, or incorrectly linked tolerances create downstream issues in procurement, planning, and assembly.
3. Tolerance misreads cascade into production and certification issues
Even small GD&T misinterpretations can affect machining strategies, inspection plans, and compliance documentation, thus leading to rework, delays, or non-conformance findings.
4. RFQ cycles slow under clarification overhead
Ambiguities in drawings trigger repeated clarification loops between engineering, suppliers, and procurement. Each iteration delays quoting, increases cost uncertainty, and reduces competitiveness in bid-driven programs.
These breakdowns are not isolated errors; they expose a structural gap in how aerospace organizations translate blueprint intent into executable data at scale.
Closing this gap requires more than process optimization; it requires an intelligence layer capable of interpreting drawings consistently across functions and programs. This is where AI enters the aerospace manufacturing workflow.
AI as a Blueprint Intelligence Layer: AI in Aerospace Manufacturing
Aerospace manufacturing demands more than high-speed OCR or generic pattern matching. It requires a true intelligence layer that interprets blueprints holistically, integrating geometry, tolerances, datums, and part relationships into actionable manufacturing data.
1. Contextual understanding over isolated symbols
Instead of reading text or shapes one by one, AI interprets aerospace drawings as a whole. It understands how dimensions, callouts, leaders, and features connect to each other, much like an experienced engineer reviewing the drawing. This allows AI to turn 2D blueprints into meaningful manufacturing insights, not just extracted text.
2. Full interpretation of GD&T, datums, and feature relationships

GD&T and datums define how aerospace parts function and fit together. AI recognizes these controls in context and correctly links them to the relevant geometry. This reduces the misinterpretation that often occurs in manual reviews and supports more consistent machining, inspection, and compliance decisions.
3. Consistent interpretation across teams and programs
A centralized AI intelligence layer applies the same interpretation logic across engineering, estimating, quality, and supply chain teams. This ensures everyone works from a single standard, even across global programs, suppliers, and long-running aerospace initiatives.
4. Handles scanned, legacy, and mixed-format drawings
Aerospace organizations often manage decades of drawings in different formats, including scanned PDFs, legacy prints, and annotated files. AI can interpret these real-world documents and convert them into structured, usable data, without requiring clean, native CAD files.
To understand how ready your aerospace drawings are for AI-driven interpretation, explore Markovate’s Blueprint Readiness Assessment to evaluate complexity, consistency, and automation potential across your blueprint portfolio.
Automating GD&T Extraction and Feature Recognition: AI in Aerospace Manufacturing at Scale
Once AI establishes blueprint intelligence, the next critical step is automated extraction of GD&T and features – a requirement for aerospace programs where precision, traceability, and repeatability are non-negotiable.
1. Automated GD&T extraction with program-level consistency
AI identifies and extracts geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) directly from drawings, mapping them accurately to the associated features and datums. This ensures consistent interpretation across ASME standards and program-specific tolerancing rules, reducing downstream ambiguity in machining and inspection.
2. Feature recognition aligned to aerospace manufacturing intent
Beyond geometry, AI recognizes manufacturing-relevant features such as holes, slots, pockets, ribs, fasteners, and interfaces. Thus, interpreting them in the context of aerospace assemblies rather than as isolated shapes.
3. Tolerance-to-feature mapping for production and quality workflows
By linking extracted tolerances directly to recognized features, AI creates a structured foundation for machining strategies, inspection planning, and certification workflows. It also supports certification workflows that are critical in regulated aerospace environments.
4. Reduction in interpretation-driven production risk
Automated extraction eliminates common failure points such as missed tolerances, misapplied GD&T, or incomplete feature identification. Such errors often lead to scrap, rework, or certification delays in aerospace programs. By enforcing consistent interpretation, AI significantly reduces these risks.
5. Scalable accuracy across large drawing volumes
Aerospace programs often involve thousands of drawings across long product lifecycles. AI applies the same interpretation logic consistently at scale, thus enabling teams to process high volumes without sacrificing accuracy or compliance.
From Aerospace Drawings to Multi-Level BOMs, Costing, and RFQ Acceleration

In aerospace manufacturing, drawings are more than design references. They serve as the system of record for parts, assemblies, compliance, and cost. Once AI structures blueprint data, it creates a direct path from engineering intent to execution.
1. Automated multi-level BOM generation from drawings
AI converts complex aerospace drawings into structured, hierarchical bills of materials, capturing parts, sub-assemblies, fasteners, and interfaces. This reduces gaps, duplication, and manual reconciliation across engineering and procurement teams.
2. Tolerance- and feature-aware cost estimation
Extracted GD&T and recognized features feed directly into cost models, enabling more accurate predictions of machining complexity, inspection effort, and certification requirements. These are critical drivers of aerospace program cost.
3. Faster, cleaner RFQ preparation for suppliers
Structured BOMs and feature data eliminate ambiguity in RFQs. Suppliers receive clearer requirements upfront, reducing clarification cycles, bid variability, and sourcing delays.
4. Improved alignment between engineering, supply chain, and quality
With a shared, machine-readable interpretation of drawings, teams operate from a single source of truth. Further, improving coordination across internal functions and external partners.
5. Scalable support for long-running aerospace programs
As programs evolve through revisions and design changes, AI updates BOMs and cost inputs consistently, helping organizations maintain control across extended product lifecycles.
Rule-Driven Intelligence for Aerospace-Grade Manufacturing Control
Aerospace manufacturing operates under strict, program-specific rules, from GD&T interpretation and material specifications to inspection methods and certification requirements. These rules vary by aircraft program, OEM, supplier tier, and regulatory framework, and they must be applied consistently over long program lifecycles.
AI-powered blueprint intelligence introduces a rule-driven approach that allows organizations to encode their interpretation standards once and apply them reliably across every drawing, revision, and supplier interaction.
Instead of relying on tribal knowledge or individual judgment, manufacturers can define:
- program-specific GD&T interpretation logic.
- tolerance thresholds tied to manufacturing and inspection capabilities.
- feature handling rules based on part criticality or certification class.
Once established, these rules are enforced automatically and consistently, whether the system processes a single drawing or thousands across multiple programs.
This rule-based intelligence supports:
- Regulatory compliance and audit readiness, with traceable interpretation logic.
- Repeatable decision-making across engineering, estimating, quality, and supply chain teams.
- Long-term scalability, ensuring interpretation standards remain intact as programs evolve and teams change
By embedding aerospace-specific rules directly into AI systems, manufacturers institutionalize expertise, reduce risk, and maintain control across complex, multi-year production environments.
How This Fits into the Full AI Manufacturing & PLM Workflow
AI-driven blueprint intelligence is most powerful when it operates within a connected manufacturing ecosystem, not as a standalone tool. In aerospace environments, structured drawing data becomes a critical input that strengthens PLM-driven workflows across the entire product lifecycle.
Once drawings are interpreted and structured, that intelligence flows naturally into:
- PLM systems, enriching product definitions with tolerance- and feature-aware data.
- Manufacturing planning, supporting accurate process selection and sequencing.
- Quality and inspection workflows, ensuring alignment with design intent and certification needs.
- supply chain and sourcing, enabling clearer RFQs and more predictable supplier responses.
This creates a continuous digital thread from design through production, quality, and procurement, anchored by a shared, machine-readable understanding of the blueprint.
Importantly, AI does not replace PLM. Instead, it acts as the intelligence layer that feeds PLM with accurate, structured inputs, eliminating manual interpretation gaps that traditionally disrupt downstream systems.
As part of a broader digital manufacturing strategy, AI-powered blueprint intelligence:
- Strengthens cross-functional coordination.
- Reduces lifecycle friction caused by drawing ambiguity.
- Supports long-running aerospace programs with consistent data foundations.
In short, in this model, AI becomes a strategic enabler, thus transforming static drawings into living data assets that support informed decisions throughout the aerospace product lifecycle.
Markovate’s Role in Aerospace Blueprint Intelligence
Aerospace manufacturers require more than point solutions; they need a reliable intelligence layer that scales across programs, suppliers, and lifecycle stages. Markovate provides this blueprint intelligence foundation for enterprise aerospace manufacturers operating high-complexity, high-volume programs.
Built on deep experience in manufacturing AI, Markovate delivers an enterprise-grade blueprint intelligence platform designed to operate within the realities of aerospace production. The focus is not on automating isolated tasks, but on standardizing, governing, and scaling how complex drawings are interpreted, structured, and operationalized across engineering, quality, and supply chain teams.
At the core of this approach is our proprietary solution BlueprintClassifier.ai, an independent, purpose-built platform that transforms complex aerospace drawings into structured, machine-readable intelligence. It is engineered to work with:
- Multi-view, high-density aerospace drawings.
- GD&T-heavy specifications and program-specific standards.
- Scanned, legacy, and mixed-format documents.
- Evolving designs and long-running aerospace programs.
Designed for regulated aerospace environments, the platform supports secure handling and traceable interpretation of drawings that may fall under export-controlled or defense-related frameworks such as ITAR and USML classifications, aligning with enterprise governance and compliance expectations.
Our AI Blueprint Classifier solution enables:
- Establish a compliance-ready, auditable interpretation layer that supports certification, traceability, and regulatory reviews
- Convert blueprint intent into structured data for BOMs, costing, RFQs, and PLM workflows
- Scale blueprint interpretation across large drawing volumes and multi-supplier ecosystems without scaling manual effort
Rather than replacing existing systems, Markovate equips large-scale aerospace programs with blueprint intelligence that connects engineering intent to execution.
This allows PLM, ERP, manufacturing, and supply chain systems to operate on accurate, consistent inputs. Thus, reducing risk, improving throughput, and supporting long-term program success.
Conclusion: AI in Aerospace Manufacturing
In aerospace manufacturing, accuracy and consistency are non-negotiable. Manual blueprint interpretation, multi-level BOM creation, and tolerance-driven costing introduce risk, delays, and inefficiency.
Markovate’s AI-powered blueprint intelligence transforms this process – turning complex aerospace drawings into structured, machine-readable data that powers BOMs, cost estimation, RFQs, and PLM workflows.
By standardizing interpretation, applying program-specific rules, and scaling across teams and suppliers, manufacturers gain faster decisions, improved alignment, and reduced operational risk.
For aerospace programs with long lifecycles and high compliance requirements, investing in AI blueprint intelligence is not just about automation; it is a great start toward enterprise-grade manufacturing excellence.
To see how AI blueprint intelligence can strengthen your aerospace manufacturing workflows, connect with Markovate to explore an enterprise-ready approach built for scale, compliance, and long-term program success.
FAQs: AI in Aerospace Manufacturing
1. How is AI used in aerospace manufacturing drawings?
AI is used to interpret complex aerospace drawings by reading GD&T, features, and part relationships in context. It converts unstructured blueprints into structured data that supports BOM creation, cost estimation, RFQs, and downstream manufacturing workflows.
2. Can AI automatically create multi-level BOMs from aerospace drawings?
Yes. AI can extract parts, sub-assemblies, fasteners, and interfaces directly from aerospace drawings to generate accurate, multi-level BOMs. This reduces manual errors, improves consistency, and accelerates procurement and planning processes.
3. Why is manual blueprint interpretation a risk in aerospace programs?
Manual interpretation varies between engineers, suppliers, and teams. In aerospace programs, this can lead to tolerance misreads, BOM gaps, RFQ delays, and compliance issues. AI helps eliminate these risks by applying consistent, auditable interpretation at scale.
markovate.com (Article Sourced Website)
#Aerospace #Manufacturing #Automating #Complex #Drawings #MultiLevel #BOMs
