The DUNEACRE 138KV – MICHIGA2 138KV transmission line, known in PJM as L765.DUMONT-WILTONCENTER.11215 and in MISO as DUNEACRE 138KV – MICHCITY 138KV (AEPCE01), is a critical bottleneck for transmission constraint in both PJM and MISO energy markets. Its sensitivity to generation shifts and outages, particularly with stronger shift factors in MISO, makes it a prime target for traders leveraging real-time grid analytics. By leveraging Enverus Grid Analytics and Forecasting Solutions, traders can harness real-time grid analytics and congestion analytics to gain actionable insights, optimize trades and stay ahead in these dynamic markets.
PJM: Nuclear and Wind Drive Congestion
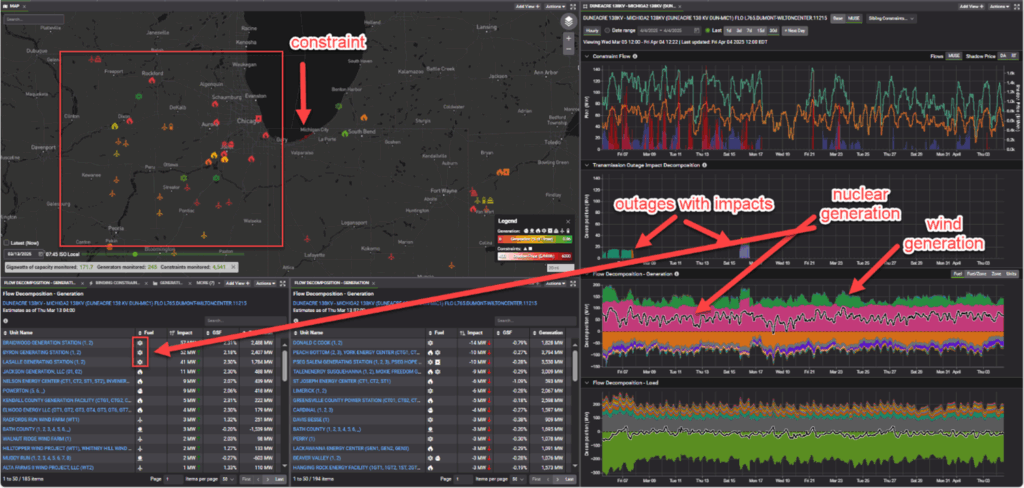
In PJM, the DUNEACRE-MICHIGA2 constraint is primarily driven by nuclear and wind generation. While certain transmission outages can increase flows on this line, they are infrequent. The constraint often binds with significant shadow prices even without these outages, indicating a persistent stress point in the grid. The reliance on nuclear and wind generation highlights the importance of monitoring these sources to anticipate congestion patterns.
MISO: Wind and Outages Amplify Flows
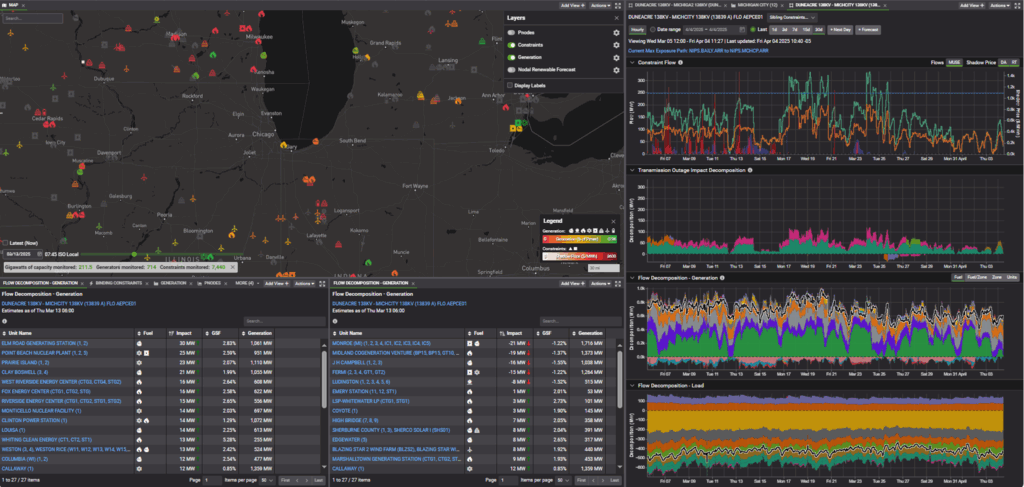
In MISO, this constraint, DUNEACRE 138KV – MICHCITY 138KV (13839 A) AEPCE01, is similarly influenced by wind generation, which is a major driver of flows on the line (seen in green in the third chart down on the right). Long-term transmission outages further exacerbate the situation, significantly increasing flows and contributing to congestion. The green, purple and orange shading in the Transmission Outage Impact Decomposition chart reveal the combined effects of these outages alongside wind generation’s role in binding the constraint.
Combined Insights: Source-to-Sink Dynamics
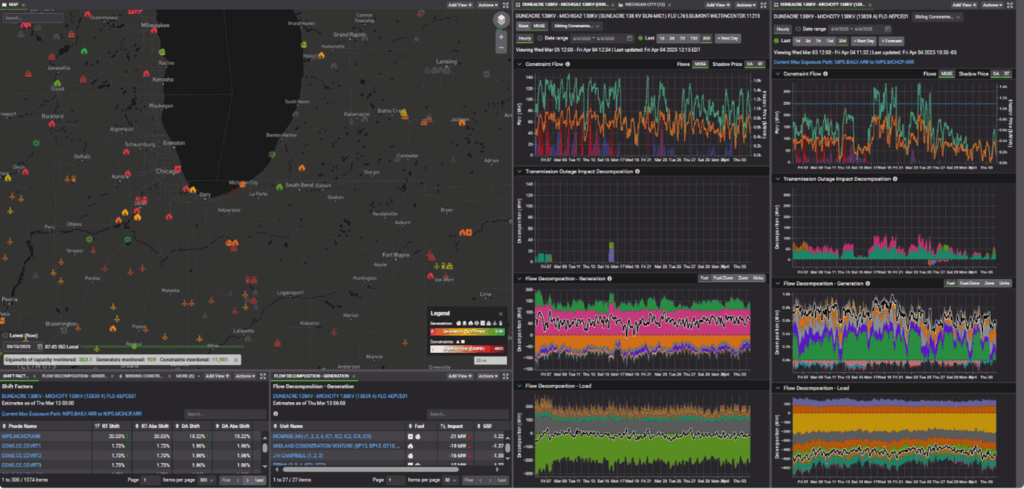
By integrating data from both PJM and MISO, we can map generation flow from the source to the sink side of the constraint. This holistic view reveals how changes in generation and outages in one market can ripple through to the other. Diving into more granular details of when source and sink side generation changes can help us better understand how small changes in active constraints can result in more confidence when it may bind stronger or weaker.
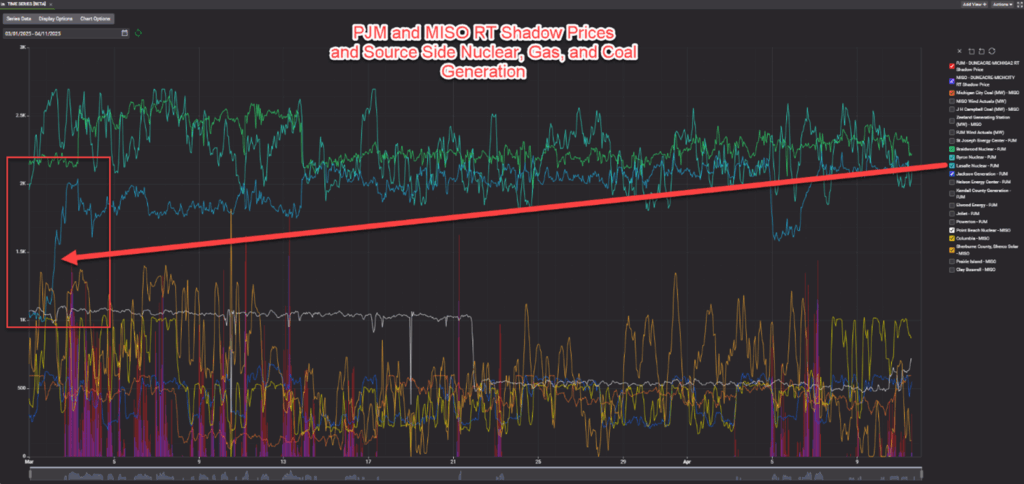
For instance, in early March, the ramp-up of a LaSalle nuclear unit in PJM led to strong binding of the constraint in both markets, underscoring the interconnected nature of these systems.
Precision Insights for Trading Success
While outages and wind generation are key drivers, congestion analytics—such as tracking unit ramp-ups or wind forecasts—sharpen predictions for the transmission constraint. Enverus real-time grid analytics deliver instant congestion insights and accurate load forecasts, enabling traders to act 75% faster on trading opportunities.
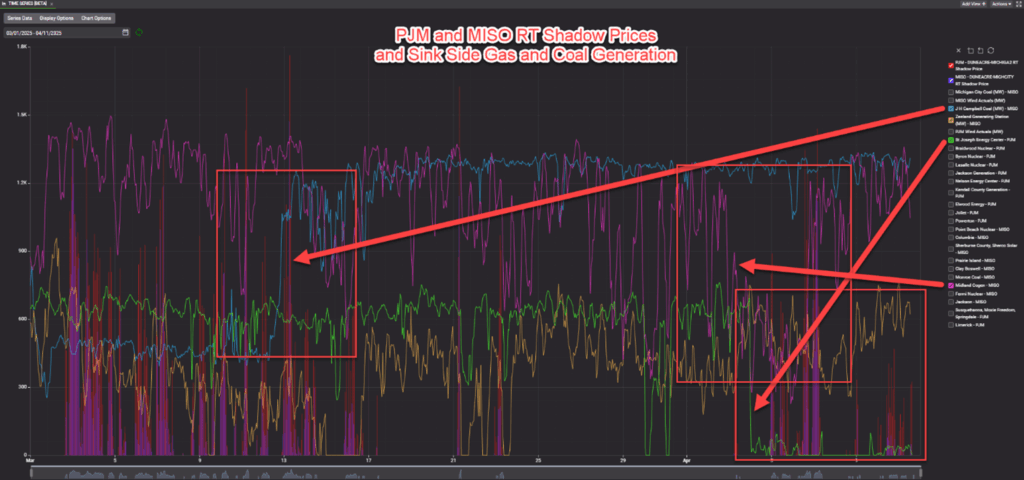
On the sink side, notable events include the offline status of the JH Campbell unit for the first half of March and the ramp-down of the St. Joseph Energy Center and Midland Cogeneration in early April. These changes coincided with a resurgence of congestion in both MISO and PJM, highlighting the sensitivity of the constraint to sink-side generation shifts.
Granular Analysis for Better Forecasting
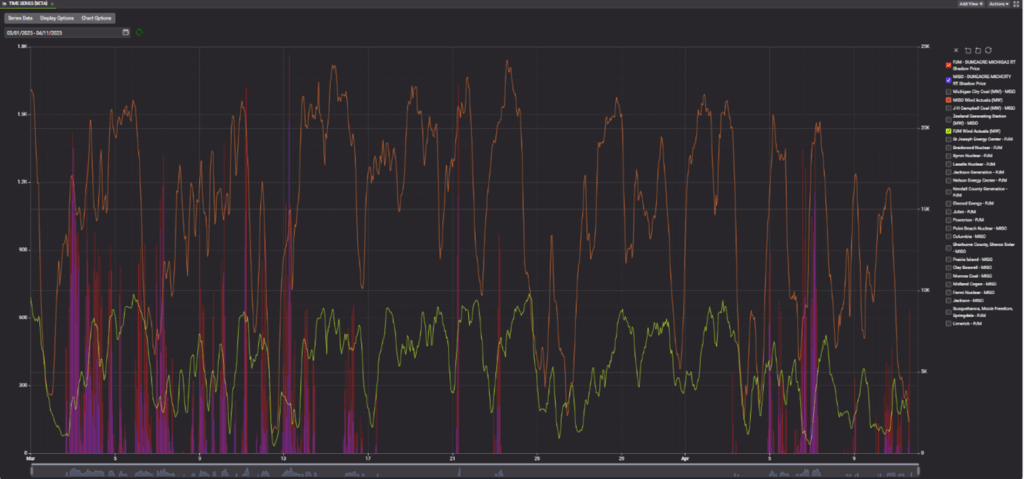
While major drivers like MISO transmission outages and wind generation are well-established, delving into granular details—such as specific unit ramp-ups or ramp-downs—can enhance our understanding of when the constraint may bind more or less intensely. For example, tracking wind forecasts in both PJM and MISO, alongside real-time generation changes, allows market participants to anticipate congestion and adjust strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
The DUNEACRE-MICHIGA2 constraint is a fascinating case study in cross-market dynamics, with nuclear and wind generation, as well as transmission outages, playing pivotal roles. By combining insights from PJM and MISO, stakeholders can pinpoint the factors driving congestion and better predict its behavior. This integrated approach not only improves operational planning but also underscores the value of cross-regional collaboration in managing complex grid constraints.
Learn How Real-Time Traders Utilize Enverus Grid Analytics and Forecasting Solutions to Find More Profitable Trades

Our comprehensive e-book is designed to elevate your power trading skills, providing essential insights and strategies to capitalize on market opportunities and manage risks effectively across all ISOs. Learn to anticipate transmission constraints, select profitable trading paths, identify optimal trading hours and understand pricing dynamics to maximize returns and maintain profitability. Packed with practical insights from industry experts, this guide equips you with proven strategies and actionable tips to navigate market challenges and achieve real-time trading success.
About Enverus Power And Renewables Grid Analytics and Forecasting Solutins
With a 15-year head start in renewables and grid intelligence, real-time grid optimization to the node and unparalleled expertise in load forecasting that has outperformed the ISO forecasts, Enverus Power and Renewables is uniquely positioned to support all power insight needs and data-driven decision-making.
The post Mastering Transmission Constraint Trading in PJM and MISO With Real-Time Grid Analytics first appeared on Enverus.
www.enverus.com (Article Sourced Website)
#Mastering #Transmission #Constraint #Trading #PJM #MISO #RealTime #Grid #Analytics
